- Home
- Core Tools Training
Core Tools Training
QC Training Services provides training workshops to give your team the foundational knowledge needed to grow your expertise in the Core Tools.
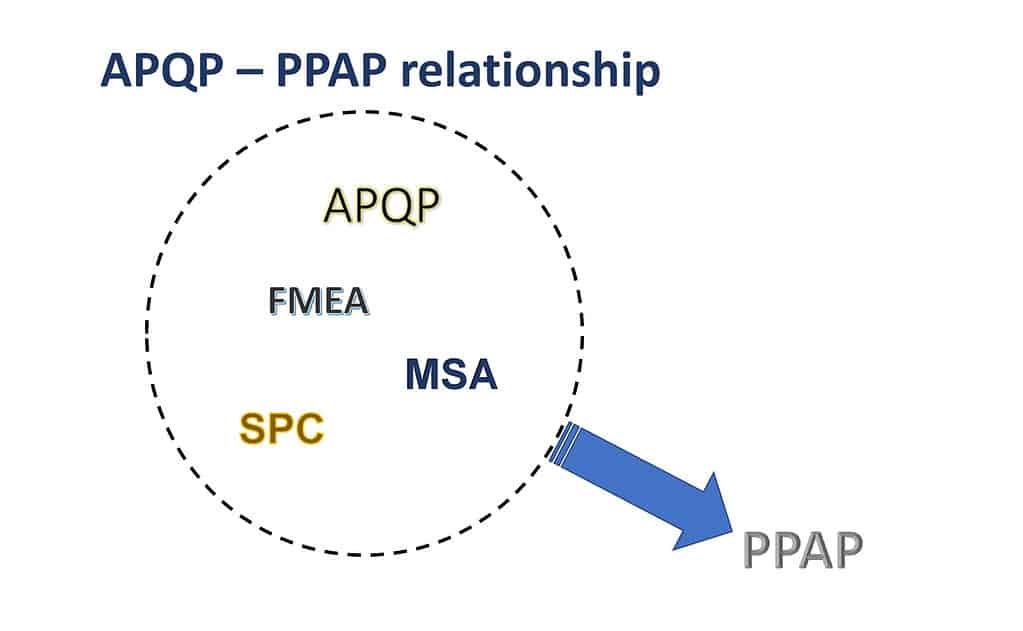

APQP & Control Plans
Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP) and Control Plans serves as a Project Management approach to reduce the complexity of product quality planning for customers and suppliers to meet performance, schedule, and cost requirements.
- APQP defines the required inputs and outputs of each stage of the product development process.
- Control Plans summarize the identified process and product parameters required to maintain process control and product conformity.


FMEA
The new AIAG & VDA Failure Mode & Effects Analysis (FMEA) Manual was developed by a global team of OEM and Tier 1 supplier subject matter experts. Design/Process/MSR FMEAs are an analytical methodology for analyzing the system and function from both a product and process perspective; and managing risks associated with it to avoid failures. What are the elements?
- The new 7-Step Approach for developing FMEAs (a paradigm shift in thinking)
- Significantly revised Severity, Occurrence and Detection (SOD) Tables.
- The new Action Priority (AP) methodology and Tables to prioritize Risks as High (Shall), Medium (Should), Low (Could) to mitigate and which actions based on the AP and SODs will achieve it
- New supplemental Monitoring System Response (MSR) FMEA for safety related monitoring systems
- New Form Sheets (spreadsheet users) and Software Report Views (software users) for use with the 7-Step Approach
- Note: Some Manufacturers are also promoting the use of Machinery FMEAs as part of Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) / Risk Management.
MSA
Quality guru Dr. W. Edwards Deming stated, “Treat all Data with Caution”. This includes the collection of data, its analysis, and providing reliable actionable information. Measurement Systems Analysis (MSA) is key to determine how much variation you actually have with the product and how much is due to the measurement system. Placing controls and making improvements with the equipment and operators will reduce uncertainty (i.e. measurement error) and increase your confidence in making robust decisions on the process and product quality. It is also important to know the capability of your measurement system before you attempt to control and improve your manufacturing processes to meet the process and product requirements.

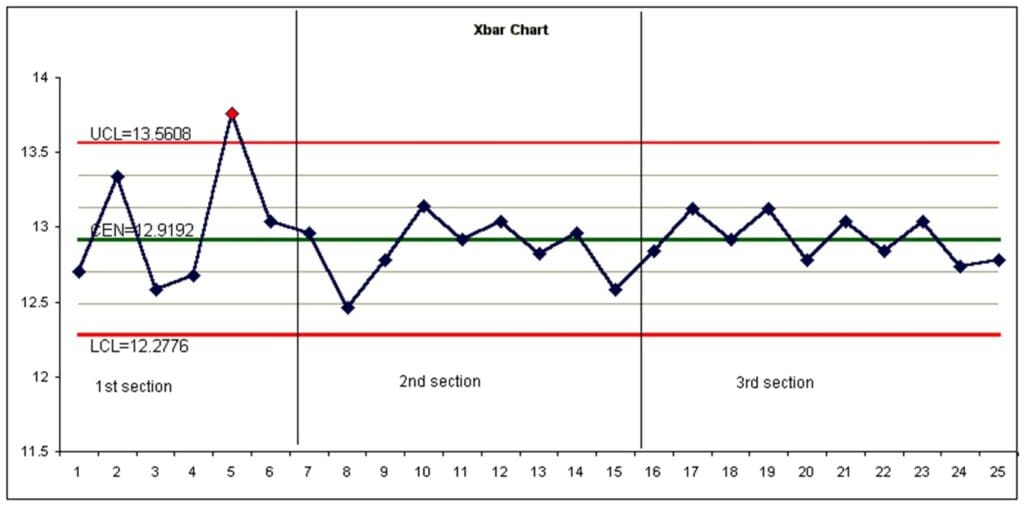
SPC and Process Capability
Statistical Process Control (SPC) was first implemented by manufacturers in the 1930s for monitoring and analyzing process to determine if it is in control and correctly determining if variation is due to special cause (i.e. abnormal behavior) or common cause (inherent behavior due to the design of the system).
By identifying and eliminating sources of special cause variation, your process will have predictable performance and you will be able to determine the Process Capabilities (i.e. Cpk) to meet requirements. If needed, you will be able to improve the inherent capabilities (i.e. use DOE to reduce common cause variation) to meet your requirements. This is important as many customers expect a Cpk ≥ 1.33 and some have raised the bar to a Cpk ≥ 1.67.
PPAP
Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) is used to ensure requirements have been met with supporting objective evidence to obtain approval for production and to obtain approval for significant changes/modifications. Use of this process between the Customer and Suppliers along with the APQP reduces delays, non-conformances, and other issues during part approval and provides confidence in the ability to consistently deliver quality parts on time and within cost constraints.